
![[Top]](../../images/home.jpg)
![[Contents]](../../images/contents.jpg)
![[Prev]](../../images/previous.jpg)
![[Next]](../../images/next.jpg)
![[Last]](../../images/index.jpg)


Setting Up Security-Card Authentication
This chapter contains:
How security cards work
You can configure your network site to require that users change passwords several times per day. When you do so, you use an external authentication server, such as a Security Dynamics ACE/Server or an Enigma Logic SafeWord server.The external server syncs up with hand-held personal security cards; these devices are typically the size of a credit card. The security card provides a user with a current password in real time. The LCD on the user's card displays the current, one-time-only password required to gain access at that moment to the secure network.
You can configure a remote authentication server supporting security cards to work with RADIUS or, in the case of the ACE/Server and Defender server, directly, without RADIUS. For information on how security card authentication using the SecurID ACE/Server without RADIUS works, see How the SecurID ACE/Server works without RADIUS and Configuring direct Defender server authentication.
Security card authentication with RADIUS
Figure 5-1 illustrates an environment that includes an Ascend Pipeline as the calling unit, an NAS (the MAX), a RADIUS server, and an external authentication server.
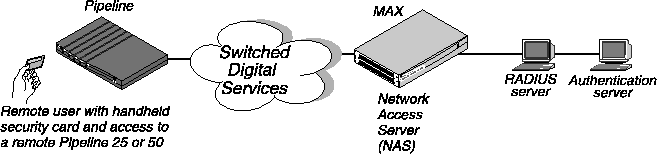
Figure 5-1. Using an external authentication server
When you use security-card authentication, these events take place:
- A user attempts to open a connection to the MAX, sending his or her username.
This user is a client of the MAX. The user can be in terminal server mode or use the APP Server utility during the authentication phase. When authentication is complete, the user can switch to PPP mode.
- The MAX determines that it must use a RADIUS user profile to authenticate the user.
- The MAX sends the user connection request to the RADIUS server in an Access-Request
packet.
The MAX is a client of the RADIUS server.
- The RADIUS server forwards the connection request to the ACE or SafeWord client
residing on the same system as RADIUS.
- The ACE client forwards the information to the ACE/Server authentication server; the
SafeWord client forwards the information to the SafeWord authentication server.
In this case, the RADIUS server is a client of the authentication server.
- The authentication server sends an Access-Challenge packet back through the RADIUS
server and the MAX to the user dialing in.
- The user sees the challenge message and obtains the current password from his or her
security card.
If the authentication server is an ACE/Server, the user has a SecurID token card that displays a randomly generated access code; this code changes every 60 seconds.
If the authentication server is a SafeWord server, the user can have one of these types of token cards:
- ActivCard
- CryptoCard
- DES Gold
- DES Silver
- SafeWord SofToken
- SafeWord MultiSync
- DigiPass
- SecureNet Key
- WatchWord
- The user enters the current password obtained from the security card in response to the
challenge message; this password travels back through the NAS and the RADIUS server
to the authentication server.
- The authentication server sends a response to the RADIUS server, specifying whether the
user has entered the proper username and password.
If the user enters an incorrect password, the ACE./Server or SafeWord server returns another challenge and the user can again attempt to enter the correct password. The server sends up to three challenges. After three incorrect entries, the MAX terminates the call.
- The RADIUS server sends an authentication response to the MAX.
If authentication is unsuccessful, the MAX receives an Access-Reject packet. If authentication is successful, the MAX receives an Access-Accept packet containing a list of attributes from the user profile in the RADIUS server's database. The MAX then establishes network access for the caller.
Direct SecurID ACE authentication
You can configure the MAX to use ACE/Server authentication without using RADIUS. The authentication process is different from authentication using the RADIUS server, and supports authentication of terminal server users only (not dial-in PPP users using the App Server). If your installation requires support for dial-in PPP users, you should configure it with RADIUS. See "Configuring the MAX to recognize the authentication server" on page 5-5.
This method is useful for installations where other RADIUS features are not required, since it decreases the complexity of the system, making it easier to configure and maintain. In addition, Direct ACE/Server authentication supports the New PIN Mode feature, which allows a dial-in user to change the personal identifying number (PIN). For information on the New PIN Mode feature, see New PIN Mode.
You can also configure ACE/Server authentication to use PAP-TOKEN-CHAP authentication. For more information, see Configuring PAP-TOKEN-CHAP using direct ACE authentication.
Understanding security-card authentication methods
You can set up SafeWord and ACE/Server security-card authentication of incoming calls using PAP-TOKEN, CACHE-TOKEN, or PAP-TOKEN-CHAP authentication. You can also specify that users request one of these authentication types when dialing out through the MAX. This section provides an overview of token-based authentication.
Setting up incoming security-card calls
When the MAX receives an incoming security-card password from a user, it must forward the authentication request to RADIUS; the RADIUS server, in turn, forwards the request to an ACE/Server or SafeWord server. The security-card caller must have a valid RADIUS user profile. Therefore, you must carry out both of these tasks:
- Configure the MAX to communicate with the RADIUS server.
- Configure a RADIUS user profile for the dial-in user.
For details on these tasks, see the MAX RADIUS Configuration Guide.
You can set up the ACE/Server for use without RADIUS. This method does not permit authentication of PPP dial-in users using the APP Server. To configure the Ace/Server to use PAP-TOKEN-CHAP authentication, see Configuring PAP-TOKEN-CHAP using direct ACE authentication.
If you are not using RADIUS see Configuring direct Defender server authentication.
Setting up outgoing security-card calls
Most sites use the MAX as an NAS for incoming security-card calls. However, you can also configure the MAX as the calling unit to allow a security-card user on the local network to call out to an NAS at a secure site.
To set up your site for outgoing security-card calls, you must complete these tasks:
- Configure the MAX to recognize the security-card authentication server.
- Configure the MAX to recognize the APP Server utility for each security-card user.
The APP Server utility enables a user to respond to token password challenges received from an external authentication server, such as an ACE/Server or SafeWord server. To allow users to supply token passwords from a host on the local network, you must configure the MAX to communicate with the APP Server utility on that host.
- Set up dial-out connections in one or more Connection profiles.
- Install the APP Server utility on each user's computer.
- Dial a connection to the remote site.
Configuring the MAX to recognize the authentication server
For the MAX to communicate with the authentication server, you must set the parameters in Table 5-1.
All of the parameters apply only to outgoing calls using security-card authentication. For the parameters to work, you must meet these conditions:
To configure the MAX to recognize the authentication server, follow these steps:
- Open the Ethernet > Mod Config > DNS menu.
- For the Password Host parameter, specify the IP address of the authentication server on
the remote network.
- Open the Ethernet > Mod Config > Auth menu.
- For the Password Port parameter, specify the UDP (User Datagram Protocol) port number
that the server indicated by Password Host is monitoring.
Valid port numbers range from 0 to 65535. The default value is 0 (zero); this setting indicates that the authentication server is not monitoring a UDP port.
- Set Password Server=Yes.
This setting specifies that callers use security-card authentication rather than terminal server authentication.
- Save your changes.
Configuring the MAX to recognize the APP Server utility
To allow users to supply token passwords from a PC or UNIX host on the local network, you must configure the MAX to communicate with the APP Server utility on that host. APP is a UDP protocol whose default port is 7001. The communication between the MAX and the host running the APP Server may be unicast (when both the MAX and the host have an IP address) or broadcast (when the host may not have an IP address).
Table 5-2 lists the APP Server parameters.
To setup the MAX to communicate with the APP Server utility, follow these steps:
- Open the Ethernet > Mod Config > Auth menu.
- Set APP Server=Yes.
This setting enables the MAX to communicate password challenges to the host running the APP Server utility.
- Specify the IP address of the host running the APP Server utility.
For example, you might enter this setting:
APP Host=10.65.212.1
If the host obtains its address at boot time from a BOOTP or DHCP server, or if it has no IP address, you can specify the IP broadcast address (255.255.255.255).
- Specify the UDP port to use for communicating with the host running the APP Server.
7001 is the default UDP port for the APP Server.If you change this number, you must specify the new UDP port number in the APP Server utility (DOS), the WIN.INI file (Windows), or the /etc/services file (UNIX). The MAX and the host running the APP Server utility must agree about the UDP port number.
- Save your changes.
Setting up a dial-out connection to a secure site
For the MAX to place calls to an NAS at a secure site, it needs the appropriate Connection profile requesting a token-based authentication type. The authentication type configured in the calling unit affects
- How the MAX transmits the token passwords
- How the user must respond when the system adds channels to an established session
The calling unit requests an authentication type, but the RADIUS daemon and RADIUS user profile accessed by the answering NAS determine the access mode to use.
Requesting PAP-TOKEN authentication
When PAP-TOKEN authentication is in use, the MAX sends the dial-out user's password in the clear (via PAP); because the password is used for one time only, sending the password in the clear does not constitute a serious security risk.
The response to the initial password challenge authenticates the base channel of the call. If bandwidth requirements cause another channel to come up, the system challenges the user for a password whenever it adds a channel to a call.
To request PAP-TOKEN authentication for an outgoing call, use the parameters listed in Table 5-3.
To request PAP-TOKEN authentication in an outgoing Connection profile, follow these steps:
- Open the Ethernet > Connections menu.
- Open the Connection profile.
- Open the Encaps Options submenu.
- Set Send Auth=PAP-TOKEN.
The Send Auth parameter specifies the authentication type requested by the caller.
- For the Send PW parameter, specify a password.
The MAX sends the value of the Send PW parameter as part of the initial session negotiation. If the session then presents a password challenge, the user types in the current one-time-only password displayed on the security card.
- Save your changes.
Requesting CACHE-TOKEN authentication
CACHE-TOKEN uses CHAP and caches the initial password for re-use in authenticating additional channels. The RADIUS profile at the remote end must contains attributes specifying how long the token remains cached. For complete information on setting up the RADIUS user profile at the remote end, see the RADIUS Configuration Guide.
To request CACHE-TOKEN authentication for an outgoing call, use the parameters listed in Table 5-4.
To request CACHE-TOKEN authentication in an outgoing Connection profile, follow these steps:
- Open the Ethernet > Connections menu.
- Open the Connection profile.
- Open the Encaps Options submenu.
- Set Send Auth=CACHE-TOKEN.
The Send Auth parameter specifies the authentication type requested by the caller.
- For the Send PW parameter, specify a password.
The MAX sends the value of the Send PW parameter as part of the initial session negotiation. The system prompts the user for a token password and uses this password to authenticate the base channel of the call via CHAP. The RADIUS server caches the encrypted password for the period specified by the Ascend-Token-Expiry attribute, or for the amount of idle time specified by the Ascend-Token-Idle attribute. When the system adds channels to a call or places a new call, it uses the cached password to authenticate the channels.
- Save your changes.
Requesting PAP-TOKEN-CHAP authentication
In PAP-TOKEN-CHAP authentication, the remote NAS uses the dynamic password the user supplies to authenticate the base channel of the call. The MAX sends the dial-out user's password in the clear (via PAP). When the MAX adds additional channels to the base channel of the call, it uses CHAP authentication for the new channels. CHAP sends encrypted passwords, so it can take the auxiliary password specified by the Aux Send PW parameter and transmit it securely.
If the calling unit request PAP-TOKEN-CHAP authentication, but the RADIUS user profile at the remote end is not set up for PAP-TOKEN-CHAP, the remote end uses PAP-TOKEN authentication instead.
To request PAP-TOKEN -CHAP authentication for an outgoing call, use the parameters listed in Table 5-5.
To request PAP-TOKEN-CHAP authentication in an outgoing Connection profile, follow these steps:
- Open the Ethernet > Connections menu.
- Open the Connection profile.
- Open the Encaps Options submenu.
- Set Send Auth=PAP-TOKEN-CHAP.
The Send Auth parameter specifies the authentication type requested by the caller.
- For the Send PW parameter, specify a password.
The MAX sends the value of the Send PW parameter as part of the initial session negotiation. If the session then presents a password challenge, the user types in the current one-time-only password displayed on the security card.
- For the Aux Send PW parameter, specify an auxiliary password.
When the MAX adds additional channels to the call's base channel, CHAP encrypts the auxiliary password specified by Aux Send PW and transmits it to the remote end.
- Save your changes.
Installing the APP Server utility
The APP Server utility enables a user to respond to token password challenges from an external authentication server, such as a Security Dynamics (ACE) or Enigma Logic (SafeWord) server.
Previous versions of the APP Server utility enabled a single user to respond to password challenges from a remote ACE/Server or SafeWord server. The current version supports multiple tokens-for a user name as well as the current password-so more than one user can use the APP Server to respond to password challenges.
Getting the right version of the utility
The APP Server utility is available for five platforms: DOS, Windows 3.1, Windows 95, Windows NT, and UNIX. The utility resides on ftp.ascend.com as a single tar archive that contains all five versions of the utility.
The tar file expands into five directories, one for each version of the utility:
- The DOS and Windows executable files are:
- appsrvds.exe (for DOS)
- appsrv31.exe (for Windows 3.1)
- appsrv95.exe (for Windows 95)
- appsrvnt.exe (for Windows NT)
- The directory contents for the Windows 95 and Windows NT versions are compressed.
- The UNIX utility is supplied as source files.
Creating banner text for the password prompt
This release incorporates a banner display facility. The banner text displays with the password prompt on the APP Server screen when you receive a challenge message. You can use the sample banner file included with this release. Or, you can specify the banner text in an ASCII file named appsrvr.ini. You can create the text file using any text editor; the file must reside in the directory in which the APP Server utility is located.
The banner can contain up to 200 characters and five lines of text. The first line of the file must contain the text "[BANNER]". For example, you might set up the file in this way:
[BANNER]
line1=The security password has changed. Please consult your
line2=card and enter the current password now.
line3=You have 60 seconds to enter the new password.
Installing the APP Server utility for DOS
To install the APP Server utility for DOS, follow these steps:
- Create an \ascend directory below the root directory.
- Copy appsrvds.exe into the \ascend directory.
- If the appsrvr.ini file exists, copy the file into the \ascend directory.
For more information on the appsrvr.ini file, see Creating banner text for the password prompt.
- Open the autoexec.bat file and add a command line to start appsrvds.exe.
The appsrvds.exe DOS utility does not require an IP stack or IP address, but it does require an ODI driver.
You must put the command line for appsrvds.exe after the line that loads the network ODI driver and before the line that loads the network protocol stack (TCP/IP, IPX, or another supported protocol). For example:
C:\novell\lsl.com
C:\novell\xxxodi.com
C:\ascend\appsrvds.exe
REM Protocol Stack is loaded next
- Close the autoexec.bat file.
- Reboot your machine.
You can specify these options on the autoexec.bat command line:
- /t - Specifies a time delay between connection attempts (in seconds).
- /y - Specifies the number of cycle counts (attempts to connect) before timeout.
- /m -Specifies the MAC address (in decimal format) of the PC running the utility.
- /p - Specifies a UDP port number for communicating with the MAX.
- /b - Specifies a UDP port for broadcast messages.
- /f - Suppresses the call at startup.
- /d - Disconnects the call.
- /c - Specifies the name of the Connection profile to use to connect to the remote secure network.
- /? -Displays a help screen.
Note: The PC sends a broadcast UDP packet that has the destination and the source port
7001, unless you specify otherwise with the /p or /b options. If you specify a number other
than 7001 in the APP Port parameter, you must use the /p or /b option to specify the same port.
If you do not specify any command-line variables, the APP Server utility uses the following default values:
- Time delay between connection attempts = 20 seconds
- Number of cycles =3 (3 times 20 seconds)
- APP Server PC MAC address = none (zeros)
- UPD port to use = 7001
- Broadcast UDP port =communication UDP port
- APP Server forces a connection upon execution.
Note: A Connection profile is required to log into the remote secure network, so if the APP
Server line in the autoexec.bat file does not specify which Connection profile to use, the
system prompts you for a Connection profile name as the system boots.
For example, consider this command line:
C:\ascend\appsrvds.exe /cChicago /t20 /p7005
This line specifies a Connection profile named "Chicago," assigns a 20-second time delay between connection attempts, and designates UDP port 7005 for communicating with the MAX.
Now, consider this command line:
C:\ascend\appsrvds.exe /cChicago /m00805110C7A44 /p7523 /t65 /b7112
This line specifies a Connection profile named "Chicago," specifies 00805110C7A44 as the MAC address of the PC running the utility, designates UDP port 7523 for communicating with the MAX, assigns a 65-second time delay between connection attempts, and designates port 7112 for sending broadcast messages (to initiate a call).
Installing the APP Server utility for Windows 3.1
To install the APP Server on a Windows 3.1 workstation, follow these steps:
- Create an \ascend directory below the root directory.
- Copy appsrv31.exe into the \ascend directory.
- If the appsrvr.ini file exists, copy that file into the \ascend directory.
For details on the appsrvr.ini file, see Creating banner text for the password prompt.
- Copy ctl3d.dll into the Windows \system directory.
We recommend adding the APP Server utility to the startup group (provided that you connect to the network as part of normal system startup). If you do not add the APP Server utility to your Startup group, you can launch the utility manually by double-clicking its icon.
To create an icon and add the APP Server to the startup group, follow these steps:
- Create a new program group in your Program Manager.
Choose File\>New\>Program Group and type:
Ascend
- Create an icon for appsrv31.exe in your Program Manager.
Choose File\>New\>Program Item.
- To launch the APP Server utility when you start Windows, place the appsrv31.exe icon in
your Startup group.
- Reboot your machine.
Installing the APP Server utility for Windows 95
To install the APP Server on a Windows 95 workstation, follow these steps:
- Copy the file xas-w95.exe into a temporary directory.
xas-w95.exe is a self-extracting zip file.
- Execute the file from the DOS shell.
The zip file expands to several files that comprise the Windows 95 Setup program.
- From the Start menu, run the Setup program in the temporary directory.
- Follow the prompts, selecting the directory in which to install APP Server for Windows
95.
APP Server for Windows 95 starts automatically whenever the system reboots. You can close the APP Server utility in a session, but next time you reboot the system, the utility starts up again. To permanently remove or disable the APP Server utility, you must edit the Windows 95 Registry to remove the key that refers to appsrv95.exe.
Installing the APP Server utility for Windows NT
To install the APP Server on a Windows NT workstation, follow these steps:
- Copy the file xas-nt.exe into a temporary directory.
xas-nt.exe is a self-extracting zip file.
- Execute the file from the DOS shell.
The zip file expands to several files that comprise the Windows NT Setup program.
- From the Start menu, run the Setup program in the temporary directory.
- Follow the prompts, selecting the directory in which to install APP Server for
Windows NT.
APP Server for Windows NT starts automatically whenever the system reboots. You can close the APP Server utility in a session, but next time you reboot the system, the utility starts up again.
There are three icons provided during installation that enable you to temporarily disable the APP Server, manually control when it runs, or remove it from the system.
Installing the APP Server utility for UNIX
To install the APP Server utility on a UNIX host:
- Edit the Makefile appropriately for your operating system and compiler.
- Compile the appsrvr source file (make).
- Add a line to the /etc/services file assigning UDP port 7001 to the APP Server utility.
To use the default UDP port 7001, add this line to the /etc/services file to document that the port is now in use:
appServer 7001/udp
If port 7001 is already assigned for a different purpose, you can use a different port for the APP Server utility by adding a line such as this to the services file:
appServer port_num/udp
The port_num argument is the port number the utility uses. Make sure you specify the same number using the APP Port parameter on the MAX.
- If the UNIX host has an IP address, you can run the utility in unicast mode by typing this
command at the UNIX prompt:
./appsvr
When you run the utility in unicast mode, it transmits packets on the specified UDP port with the source address set to its own IP address. When the MAX receives those packets on the specified UDP port, it returns packets to the specified IP address.
- If the UNIX host does not have an IP address (for example, if it obtains its address from a
BOOTP or DHCP server), run the utility in broadcast mode by typing this command:
./appsrvr -b
The -b argument sets a socket option to allow broadcast transmissions and inhibits the utility's complaints about receiving invalid APP frame types when it receives its own transmissions.
Note: On some UNIX systems, you need root privileges to run the APP Server utility in
broadcast mode. Some hosts disallow broadcast transmissions without root privileges. If you
are running the utility in broadcast mode, make sure that the MAX is configured with the
broadcast address in the APP Host parameter (APP Host=255.255.255.255).
Dialing a connection to a secure site
This sections describes how to initiate a connection to a remote network from different types of platforms.
Connecting to a remote network from the terminal server
To make an outgoing call to a secure site from a terminal server session, follow the steps described in this section. For a modem connection, begin the process at step 2.
- At the terminal server prompt, enter this command:
set password
The following message displays:
Entering Password Mode...
The prompt changes to the display following text:
[^C to exit] Password Mode>
- Bring up a connection to the secure site in one of these ways:
- Start a program that requires a connection to a host on the remote network.
- Use the DO menu on the MAX.
- Dial the remote NAS via modem
The remote NAS returns a challenge prompt that looks like this one:
From: hostname
0-Challenge: challenge
Enter next password:
hostname is the name of the NAS you are calling; it is optional on some systems.
If the Send Auth parameter is configured incorrectly, no challenge prompt appears, or you see an error message such as this one:
From: hostname
Received unexpected PAP Challenge!... check PPP Auth Mode
- At the challenge prompt, enter the password obtained from your security card.
You have 60 seconds to enter the password correctly. When you enter the correct password, the MAX establishes the connection to the secure network. If you do not specify the correct password within 60 seconds, the login attempt times out. If you enter the password incorrectly, the challenge prompt displays again, up to three times.
- To return to normal terminal server operations, press Ctrl-C at the Password Mode prompt.
Connecting to a remote network from a DOS workstation
To initiate a connection to a remote secure network, you reboot the PC. After the initial session negotiation, the remote ACE/Server or SafeWord server returns a password challenge that looks similar to this one:
From: hostname
0-Challenge: challenge
Enter next password:
hostname is the name of the NAS the user is calling; it is optional on some systems.
If the Send Auth parameter is configured incorrectly, no challenge prompt appears, or you see an error message such as this one:
From: hostname
Received unexpected PAP Challenge!... check PPP Auth Mode
You have 60 seconds to enter the password correctly. When you enter the correct password, the MAX establishes the connection to the secure network. If you do not specify the correct password within 60 seconds, the login attempt times out. If you enter the password incorrectly, the challenge prompt displays again, up to three times.
If more than one user uses the APP Server to log into a remote secure network through the MAX, each user must include a user name in this format:
password.username
Connecting to a remote network from a Windows workstation
The user interface is the same for all Windows versions of the APP Server utility. To use the Windows utility, follow these steps:
- Start the utility by using the Services applet on the Control Panel.
- In the dialog that displays, click Connect.
The Settings dialog box opens.
- Enter the name of the Connection profile used to log into the remote secure network.
- Enter your username.
You can specify up to 32 characters; you cannot enter spaces.
- Click OK.
After the initial session negotiation, the remote ACE/Server or SafeWord server returns a password challenge; the challenge displays in its own dialog box. You have 60 seconds to obtain the current dynamic password from the security card and enter it correctly.
- Type the current password and click OK.
- To log out of the remote network, click Disconnect.
- In the dialog that displays, type the name of the Connection profile that defines your
connection to the remote network; then, click OK.
Connecting to a remote network from a UNIX workstation
When you start an application that requires a connection to a host on a secure network, the MAX initiates a call. After the initial session negotiation, the remote ACE/Server or SafeWord server returns a password challenge that looks similar to this one:
From: hostname
0-Challenge: challenge (or null challenge, depending on your
setup)
Enter next password:
hostname is the name of the NAS you are calling; it is optional on some systems.
If the Send Auth parameter is configured incorrectly, no challenge prompt appears, or you see an error message such as this one:
From: hostname
Received unexpected PAP Challenge!... check PPP Auth Mode
You have 60 seconds to enter the password correctly. When you enter the correct password, the MAX establishes the connection to the secure network. If you do not specify the correct password within 60 seconds, the login attempt times out. If you enter the password incorrectly, the challenge prompt displays again, up to three times.
If more than one user uses the APP Server to log into a remote secure network through the MAX, each user must include a user name in this format:
password.username
How the SecurID ACE/Server works without RADIUS
Users dialing into a MAX who are authenticated by a SecurID ACE server directly (without RADIUS) can specify one of the MAX unit's local profiles to be used for session parameters. When a user dials into the MAX, the usual banner and prompt appear: For example:
** Ascend Pipeline Terminal Server **
Login:
When the user enters a name, the screen prompts for a password, just as for a "normal" login without:
Password:
At this point, the user must enter his or her PIN, followed by the numbers currently being displayed on the SecurID token card.
Note: Unlike the SecurID ACE support in RADIUS, which ignores the input to "Password:"
and asks for a "Passcode," this direct implementation does not take the extra step. The Ascend
unit sends the input to the Password prompt to the ACE server as the passcode. If you want the
Ascend unit to ask for a passcode, you can change the password prompt using the Password
Prompt parameter in the TServ Options submenu of the Ethernet Profile.
If the login is correct, the terminal server prompt appears:
ascend%
If the login is incorrect, this message appears:
** Bad Password
The Ascend unit requests another login. This process repeats three times, or until the user enters a valid login name/password (or passcode) combination.
NextCode Mode
If a particular user has three or more consecutive incorrect logins, the server marks that user's token card as being in "NextCode" mode. When the user finally logs in successfully, he or she must enter in an extra passcode from his or her token to verify actual possession of the token card. When the user has sent his or her first correct PIN + passcode to the Ascend unit, this message appears:
Wait for the code on your token to change, then enter the new
code (without PIN).
Passcode:
The user must then wait until the number displayed on the token card changes, and then type in that number without the PIN. If the user enters a correct code, the terminal server command prompt or menu appears. If the user enters an incorrect code, the Ascend unit displays a "**Bad Password" message and the user's token remains in "NextCode" mode.
New PIN Mode
The ACE server system administrator can place particular tokens in "New PIN" mode. The next time the user successfully authenticates and wants access to the system, he or she must choose a new PIN or allows the server to generate one.
After the normal authentication, the Ascend unit displays one of the following three messages.
- If the server was configured to allow the user to choose a new PIN or request one from the
server, this 5-line message displays:
Enter your new PIN, containing 4 to 8 digits:
or
<Return> to generate a new PIN and display it on the screen:
or
<Ctrl C> to cancel the New PIN procedure:
Note: The number of allowed digits may change according to the server configuration; the
server can also be configured to allow alphabetic characters in the PIN, in which case the word
"characters" appears in place of "digits" in the first message.
- If the server was configured to force the user to choose his or her own PIN, this message
displays:
Enter your new PIN, containing 4 to 8 digits:
- If the server was configured to restrict the user from choosing a PIN, and to always
generate a random PIN for the user, this message displays:
Press <Return> to generate a new PIN and display it on the screen:
User-chosen PIN
In cases 1 and 2, when the user enters a new PIN, the server checks the PIN. If the new PIN has the appropriate number of characters or digits, the Ascend unit asks the user to retype the same PIN for verification:
Please re-enter new PIN:
The user types in the new PIN. If the PINs match, the new PIN is sent to the server, and the user is informed that the PIN has changed:
Wait for the code on your token to change, then log in with the
new PIN
Login:
If, after the second verifying PIN entry, the Ascend unit sees that the user entered two different PINs, this message appears:
PINs do not match. Please try again.
Login:
The user must log in again. The server then asks the user to choose a new PIN.
Server-chosen PIN
In cases 1 and 3, when the server generates a PIN for the user, the user simply presses Enter in response to the initial "New PIN" prompt. The server then displays this question:
ARE YOU PREPARED TO HAVE THE SYSTEM GENERATE A PIN? (y or n)
[n]:
If the user presses "y" or "Y", the screen displays a new PIN chosen by the ACE server:
Your new PIN: 6467
Press Enter to clear screen:
The user must immediately memorize the PIN, and then press Enter. The screen clears, the PIN is sent back to the Ascend unit for confirmation, and if the ACE server accepts the PIN, the Ascend unit displays this message:
Wait for the code on your token to change, then log in with the
new PIN
Login:
Note: Changing your PIN counts as one of the three allowed logins per dialup, so a correct
PIN change followed by a login counts as two attempts. Therefore, if you fail twice, you need
to redial and connect in order to complete authentication.
Configuring direct SecurID ACE authentication
This section describes how to configure a SecurID ACE server as your MAX's external authentication server. When you configure the ACE server as an external authentication server, any calls that are not authenticated by local Connection profiles are forwarded to the ACE server for authentication. If you requires your MAX to reach more than one authentication server, see the RADIUS Configuration Guide. Other software products, such as Ascend's Access Control, support multiple external authentication servers through the MAX. Although SecurID ACE authentication is indirectly supported via RADIUS, direct support for the SecurID ACE server can be useful for two main reasons:
- For those installations where other RADIUS features are not required, direct SecurID
ACE support on the Ascend unit decreases the complexity of the system, making the
system easier to configure and maintain.
You can specify one of the MAX unit's local profiles to be used for session parameters with ACE authentication, and configure different profiles/addresses for each user based upon whether the user has dialed in with a modem (analog call) or ISDN (digital call). You can also specify a Lan Address setting that overrides the Lan Address in the specified profile (or in the default profile, if no specific profile is given). This means that you can specify two different remote settings for a user with a single token card. See
To configure the MAX for direct authentication using a SecurID ACE server, follow these steps:
- Open the Ether > net > Mod Config > Auth menu:
X0-X00 Mod Config
Auth
>Auth=SECURID
Auth Host #1=137.175.80.24
Auth Host #2=0.0.0.0
Auth Host #3=0.0.0.0
Auth Port=2626
Auth Timeout=10
Auth Key=N/A
Auth Pool=No
APP Server=No
APP Host=N/A
APP Port=
SecurID DES encryption=N/A
SecurID host retries=N/A
SecurID NodeSecret=N/A
- Set Auth to SECURID.
Auth Host #2 and Auth Host #3 are not applicable, because the Ascend unit can support only one SecurID ACE authentication server at this time.
Note: For a SecurID server to authenticate an AppleTalk Remote Access (ARA) caller
through RADIUS, set Auth=RADIUS/LOGOUT. See Setting up ARA authentication for
more information about setting up a ARA connection through RADIUS.
- For the Auth Port parameter, enter the UDP port number used by the SecuridID ACE
server.
For example, you might specify this setting:
Auth Port=1545
- To specify the number of seconds the MAX waits for a response to an authentication
request, set the Auth Timeout parameter.
If the MAX does not receive a response within the time specified by Auth Timeout, it assumes the SecurID ACE server has become nonfunctional.
- To specify whether the server uses standard DES or the native encryption provided by
SecurID, choose one of the following values for SecurID DES encryption parameter:
- Yes specifies that the server uses standard DES encryption.
- No specifies that the server uses the native encryption provided by SecurID.
- To specify the number of times the Ascend unit attempts to contact the SecurID host
before timing out, enter an integer in the SecurID Host Retries parameter.
The default value is 3.
- Set the SecurID Node Secret parameter.
For details on this parameter, see the MAX Reference Guide.
Configuring user shell settings on the ACE server
You can configure a shell setting for each user on the ACE server to store several parameters about the user, including the name of a MAX local profile which should be used when setting up the call for that user, as well as the address and netmask to be used in place of the Lan Address in the given profile.
Shell string structure
The shell string returned by ACE is limited to 64 characters, so brevity is very important. The names of parameters are extremely short. The basic structure of the string is:
<parameters> |<CallType> <parameters> |<CallType> <parameters> ...
Conventions
The conventions in the following table apply to all strings.
Examples of String Contents:
For example, the following string
|D prf="isdnroute" rp=[greco] la=192.0.2.1/24 |A prf=modemroute
specifies:
- if the caller is digital
- use the profile called isdnroute
- set the Receive PW to greco
- set the Lan Addr to 192.0.2.1/24
- if the caller is analog
- use the profile called modemroute
Shortening a string
The above string is just short enough to fit. If the string was any longer, the end of modemroute would be cut off and authentication would fail for analog calls. The same shell string could be given as:
|D prf=isdnroute rp=greco la=192.0.2.1|A prf=modemroute
Although this example specifies the same information as the previous example, it has been shortened in the following ways:
- The quotation symbols have been removed. In general, quotes are needed only if there is a space in the character string.
- The space has been removed from before the |A (the | character indicates the end of a string, just like a space).
- The netmask was not given (/24 is the default netmask for 192.0.2.1, a class C network address).
Setting common parameters for analog and digital calls
It is also possible to have common parameters preceding the sections specific to just analog or digital. For example:
prf=john |D la=135.2.2.4/24 |A la=135.2.3.20
In this example, the settings would always be taken from the profile john, but the address would be set differently depending on whether the call was analog or digital.
The section with common parameters can be placed after the specific sections as well as before. For example, the following string:
|A prf=modemroute |D prf=isdnroute | la=10.0.0.20/32
says to use modemroute as the profile template for analog calls, isdnroute for digital calls, and in both cases to use the address 10.0.0.20/32 as the LAN Address.
Separate sections are not required. For example:
prf=john la=10.0.0.20/32
would use the profile named john and set the Lan Address to 10.0.0.20/32 whether the call was analog or digital.
Or you can have just one or the other:
|D prf=isdnroute rp= "go for it"
In this case, an analog caller would be given the default or answer profile depending on the setting of the Use Answer as Default parameter in the answer profile.
String errors
If there is an error or unrecognized string in the shell string for a user, the authentication will fail. If you have trouble seeing what caused the failure, enter the MAX's debug mode and turn on a diagnostic display of the string interpretation using the command securiddebug. This is a toggle that turns the display on and off.
String too long
Check to see that you have not exceeded the 64 character limit (the ACE server's sdadmin program does not check for this limit). This is indicated when the final parameter is not complete. For security reasons, the password string is not displayed by this debug mode.
For security reasons, the password string is not displayed by this debug mode, so you will not be able to tell directly from the debug output whether the rp parameter is being truncated. If you encounter problems with the 2nd and subsequent channels of an MP call automatically authenticating, the problem could be that the end of the rp parameter is being cut off.
Setting overwritten
Each new parameter is copied over the current state of the caller's profile at each step. It is therefore possible to overwrite one setting with another. For example:
rp=joebob prf=john
will cause the Receive Password joebob to be overwritten by the Receive Password in the profile john. Be careful always to list prf's before rp's or la's.
Configuring PAP-TOKEN-CHAP using direct ACE authentication
PAP-TOKEN-CHAP stores a static password in the user's shell setting on the ACE server and sends it back to the MAX when the user first connects. Except for this, PAP-TOKEN-CHAP configuration on the calling router is identical to configuring PAP-TOKEN-CHAP for any other type of token card authentication.
To set the static password to use during PAP-TOKEN-CHAP for a particular user:
- Run the sdadmin program on the ACE server machine.
- From the Client menu, select Edit.
- Pick the MAX from the list of clients and click OK.
- Click User Activations.
- From the Directly Activated Users list, select the one using PAP-TOKEN-CHAP, then
click Edit Activation Data.
- In the Activation Data window, delete any existing text in the Shell field, and replace it
with:
rp="password"
where password is the password to be configured as the Aux Send PW on the calling router (usually a Pipeline). This is done in step 8.
For example, if you type
rp="Little Big"
in the Shell field (with quotation marks), the password the user types is
Little Big (without quotation marks).
In this example, the quotes are delimiters for the password. Different delimiters are allowed is so that the user can choose a password containing those delimiters, for example:
rp='Quote"quote'
which contains a double quote in the middle of the password.
You can use any character you like for the delimiters in place of the double quotes except the vertical bar ("|"), which has a special meaning in the shell field. For example, the following entry would produce the same Receive Password setting as rp="Little Big":
rp=/Little Big/
However, rp=[Little Big] is not identical and would an produce error, since the left bracket and right bracket are different characters.
- Press OK to clear the Activation Data dialog, and Exit to clear the Edit Client dialog
- Configure the calling router (usually a Pipeline) to use PAP-TOKEN-CHAP
authentication, and set Aux Send PW in the Connection profile Encaps options to be
identical to the string you entered in the ACE server as rp (Receive Password) in step 6.
Assuming all other configuration is already done (configuring the answering MAX to use SecurID authentication, and configuring the calling router to use the App Server, for example), you should now be able to bring up a multi-channel call, while only performing a single token authentication.
Configuring direct Defender server authentication
This section describes how to configure the Defender as your MAX's external authentication server. When you configure the Defender as an external authentication server, any calls that are not authenticated by local Connection profiles are forwarded to the Defender server for authentication. If you requires your MAX to reach more than one authentication server, see the RADIUS Configuration Guide. Other software products, such as Ascend's Access Control, support multiple external authentication servers through the MAX.
Note: The Defender server does not provide per-user control, such as enforcing a maximum
number of channels. It provides only per-user authentication. If you need both per-user control
and authentication, you need RADIUS.
How Defender server authentication works
There are three major stages in authentication using AssureNet Pathways' Defender. The MAX' behavior will depend upon the stage the call dialing the MAX was in when the connection with the host is lost.
When no authentication host is available
When a MAX can not establish contact with any of the authentication hosts in the list, all sessions are dropped, including calls in Stage 1.
If a caller who has been disconnected tries again to make a connection, the MAX will begin again the process of connecting to authentication hosts on the list until it either succeeds or has tried every host in the list.
To configure a Defender server for direct authentication, follow these steps:
- Open the Ethernet > Mod Config > Auth menu:
X0-X00 Mod Config
Auth
>Auth=Defender
Auth Host #1=137.175.80.24
Auth Host #2=0137.174.81.0
Auth Host #3=0137.174.80.25
Auth Port=2626
Auth Timeout=10
Auth Key=****************
Auth Pool=No
APP Server=No
APP Host=N/A
APP Port=N/A
SecurID DES encryption=N/A
SecurID host retries=N/A
SecurID NodeSecret=N/A
- Set Auth to Defender.
- Specify up to three authentication hosts for the Auth Host # parameters.
- Set the value of Auth Port to the TCP port number of the Defender authentication server,
usually 2626.
- Set the value of Auth Key.
Auth Key is used as a DES secret key shared between the Ascend unit and the Defender authentication server. This key is also used for authentication by the Ascend unit in its role as a Defender authentication agent.
- Set Auth Timeout to indicate the number of seconds the Ascend unit waits before
assuming that the Defender server has become nonfunctional.
- Enter the port number for the source port for remote authentication requests.
Type a port number between 0 and 65535. The default value is 0 (zero); if you accept this value, the Ascend unit can use any port number between 1024 and 2000.
You can specify the same port for authentication and accounting requests.
- Normally APP Server = No. APP Server only applies when the MAX makes outgoing
calls to MAXs and other sites using token card authentication. See the MAX Reference
Guide for more information.
- If the MAX must make outgoing calls to other MAX units and to other sites using token-
card authentication, you may need to set APP Server=Yes. Normally this parameter is set
to APP Server=No. For more details see the MAX Reference Guide.
- Save your changes.
![[Top]](../../images/home.jpg)
![[Contents]](../../images/contents.jpg)
![[Prev]](../../images/previous.jpg)
![[Next]](../../images/next.jpg)
![[Last]](../../images/index.jpg)


techpubs@eng.ascend.com
Copyright © 1998, Ascend Communications, Inc. All rights
reserved.

