
![[Top]](../../images/home.jpg)
![[Contents]](../../images/contents.jpg)
![[Prev]](../../images/previous.jpg)
![[Next]](../../images/next.jpg)
![[Last]](../../images/index.jpg)


Quickstart
This chapter explains how to perform a basic configuration of your MAX. This chapter covers these topics
Quickstart for T1 MAX units
With this Quickstart, you will be able to perform a basic configuration of your MAX. It explains how to:
- Configure your MAX for the local Ethernet
- Configure your T1 line for either inband signaling or ISDN D-channel signaling
- Test your T1 line by performing a self test
- Telnet to the MAX from a workstation to verify it is accessible over the Ethernet
- Create a Connection profile on the MAX for a remote device (such as an Ascend Pipeline) dialing in with its own IP address or for a remote device (such as a modem) that accepts a dynamically assigned address
- Provision your line for T1, PRI, or BRI access
This Quickstart does not cover more detailed configuration such as security, RADIUS, or advanced WAN or LAN protocols. Refer to the MAX 6000 Series ISP & Telecommuting Configuration Guide to perform more advanced configuration of your MAX.
Setting up your hardware
Before beginning, make sure you have:
Figure 3-1 illustrates the hardware set up you must have to use this Quickstart.
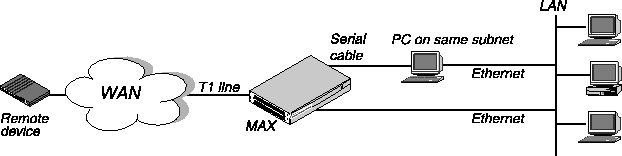
Figure 3-1. Quickstart set up
Overview of T1 line configuration
Figure 3-2 has two hunt groups-one for digital calls and one for analog calls. If you are using inband signaling, the example hunt group contains 12 channels. Analog callers call in using the phone number 555-1111 and are routed to the digital modems in slot 5. Digital callers call in using the phone number 555-2222 and are routed to the MAX bridge/router module in slot 9. This requires that you configure the Ch n slot parameter in the T1 Line profile.
Inband signaling is less flexible than ISDN D-channel signaling because you must pre-allocate the number of T1 channels used for voice and data calls. If 12 analog callers are dialed in, subsequent analog callers are rejected because there are no more channels available for analog calls, even though there are 12 unused channels.
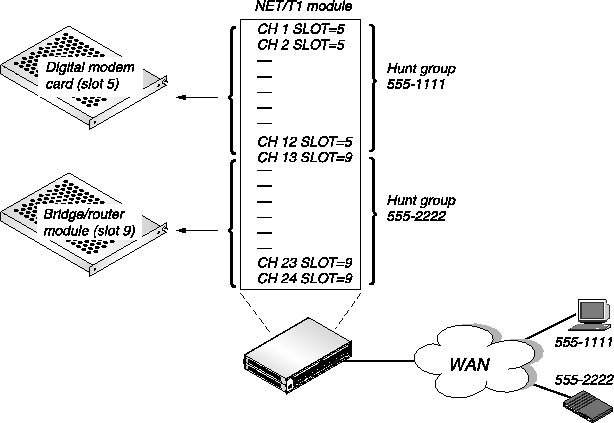
Figure 3-2. Incoming call routing using inband signaling and hunt groups
If you are using ISDN D-channel signaling (Figure 3-3) the example hunt group contains 24 channels. Analog callers call in using the phone number 555-1111 and are routed to the digital modems in slot 5. Digital callers call in using the phone number 555-2222 and are routed to the MAX bridge/router module in slot 9. This requires that you configure the Ans# parameter in the Modem profile and in the Ethernet Mod Config profile.
Incoming ISDN calls contain information about whether the call is an analog voice call (from a modem) or a digital data call. The MAX can automatically route calls to the digital modem card if the call is a voice call, or to the bridge/router module if the call is a digital call.
With ISDN signaling the hunt groups overlap the T1 channels, allowing each channel to answer either voice calls or data calls.
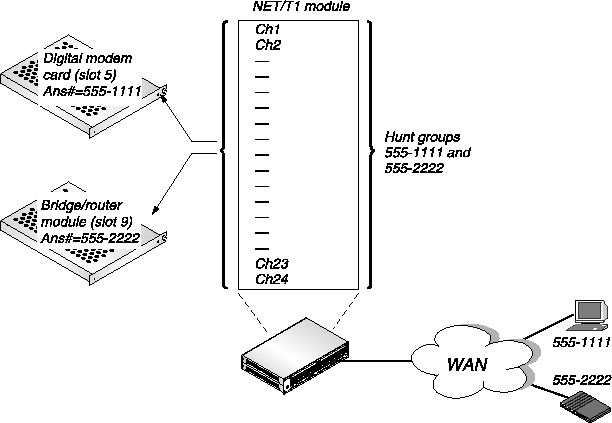
Figure 3-3. Incoming call routing using ISDN signaling and hunt groups
Gathering configuration information
In addition to the hardware set up, you must gather this configuration information about your network set up:
T1 line information
Use information in Table 3-1 to configure the MAX T1 line. You can leave all other parameters in the Line Config profile at their default values for the purposes of this Quickstart Guide.
Refer to the MAX 6000 Series Reference Guide for detailed information on the parameters in the following table.
Connection profile information
The MAX uses Connection profiles to allow access to remote devices. For this test you can set up two kinds of connections:
- A Connection profile for a remote device (such as an Ascend Pipeline) dialing in with its own IP address
- A Connection profile for a remote device (such as a modem) that accepts a dynamically assigned address
Use information in Table 3-2 to create a connection to a remote device. You can leave all other parameters in the Connection profile at their default values for the purposes of this Quickstart Guide. Refer to the MAX 6000 Series Reference Guide for detailed information on the parameters in the following table.
Ethernet profile information
Use information in Table 3-3 to configure the MAX for your Ethernet LAN. You can leave all other parameters in the Ethernet > Mod Config profile at their default values for the purposes of this Quickstart Guide. Refer to the MAX 6000 Series Reference Guide for detailed information on the parameters in the following table.
Using the MAX VT-100 interface
This section briefly introduces the MAX configuration interface. Refer to the Chapter 4, "Navigating the User Interface," for complete information on using this interface.
To perform the initial configuration of the MAX, connect a serial cable to the MAX control port and set your terminal emulation package in your communications software as follows:
- 9600 bps
- 8 data bits
- No parity
- 1 stop bit
- No flow control
- Direct connect
After communication has been established, the Control Monitor screen appears (see Figure 3-4). This interface consists of an Edit menu and eight status displays. The Edit menu allows you to configure the MAX; the status windows allow you to monitor the MAX status.
Note that the items listed in the Main Edit menu differ depending on the system configuration.
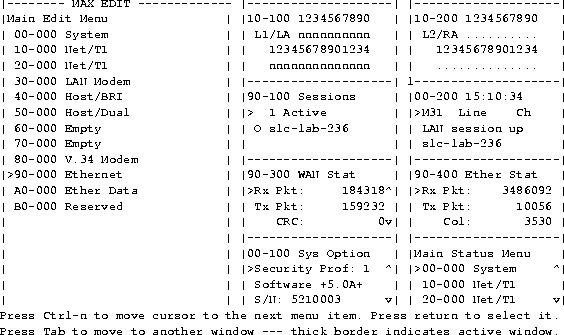
Figure 3-4. MAX configuration interface
The table below provides a quick reference for navigating the MAX user interface.
Configuring the MAX
The following configuration establishes enough functionality to verify that the MAX is up and running, connected, and can perform basic functions. You must perform the tasks in the order they are presented in this section.
The Quickstart configuration involves modifying the following profiles:
This procedure assumes you have not yet configured the MAX; therefore, all parameters initially are at their factory default settings. Do not turn the MAX off during this procedure.
Note: The question marks (??) that may appear in the upper right-hand corner of the Edit
screens and status windows indicate that there is no link to the T1/PRI line. Once you have
configured the T1/PRI line these question marks will disappear.
Configuring the T1/PRI lines
To configure a T1 line with the information you gathered in Table 3-1:
- From the Main Edit Menu, select the slot that contains your Net/T1 card, for example, 10-
000.
10-000 Net/T1
>10-100 Line Config
10-200 Line Diag
- Select Line Config.
10-100 Line Config
>10-1** Factory
10-102
10-103
10-104
- Select the currently active Line profile, 10-1** Factory.
10-1** Factory
>Name=
1st Line=Trunk
2nd Line=Disabled
Line 1...
Line 2...
- Select Line 1.
10-1** Factory
Line 1...
>Sig Mode=Inband ^
NFAS ID num=N/A
Rob Ctl=Wink-Start
Switch Type=N/A
Framing Mode=D4
Encoding=AMI
FDL=N/A
Length=N/A
Buildout=0 dB
Clock Source=Yes
Pbx Type=N/A
Delete Digits=N/A
Add Number=N/A
Call-by-Call=N/A
Ans #=N/A
- Set the appropriate signaling mode for Sig Mode parameter:
- If you selected ISDN_NFAS above, enter the NFAS ID for your line.
- If you selected Inband above, select the type of robbed bit control for the ROB Ctl.
parameter.
- N/A: This parameter is not applicable whenever the Sig Mode=ISDN.
- Wink-Start
- Idle-Start
- Inc-W-200
- Inc-W-400
- Loop-Start
- If you selected ISDN above, select the WAN switch type at the lines' point-of-presence.
- N/A: This parameter is not applicable whenever Sig Mode=Inband.
- AT&T
- NTI
- NI-2
- GloBanD
- Japan
- Select the type of framing this line uses:
- Select the encoding used on this line:
- None: This is identical to AMI, but without density enforcement.
- AMI
- B8ZS
- Select the FDL (Facility Data Link) used on this line:
- N/A: This parameter is not applicable whenever Framing Mode=D4.
- None
- AT&T
- ANSI
- Sprint
- Select the cable distance between MAX and the WAN interface equipment.
- N/A: This parameter is N/A if the MAX has an internal CSU.
- Otherwise: Select the correct cable distance in feet between MAX and the CSU or other network (WAN) interface unit to which it is connected. The default is 1-133.
- Select the amount of attenuation to add to the line's network interface:
- N/A: This parameter is N/A if the MAX does not have an internal CSU.
- Otherwise: Select the Buildout value to provide the proper line attenuation. The default is 0db.
- If your channels are not switched (the default), specify how the MAX uses the T1
channels using the Ch n parameter:
- Switched (the default)
- Nailed (dedicated)
- Unused (not in service)
Note: To test the line later, you must have at least two switched channels. If you plan to
use a channel for drop-and-insert (D&I), you can enter it as Switched for the Quickstart
and then change it to D&I for the final installation.
- If you using inband signaling, configure incoming call routing for the T1 line by setting
the following parameters:
- For each Ch n # parameter, enter the rightmost unique digits of the phone number used to reach this channel.
- For example, if your line is set up as illustrated in Figure 3-2 on page 3-3, enter 1111 for the first 12 channels (the analog call hunt group), and 2222 for the last 12 channels (the digital call hunt group).
- For each T1 channel that will answer analog calls, set the Ch n Slot parameters to the number of the slot that contains the modem card.
- For example, if the modem card is in slot 5, set Ch 1 Slot=5, Ch 2 Slot=5, and so on, up to the total number of analog calls you want the MAX to accept on this T1 line. This tells the MAX to route incoming analog calls to the digital modem card.
- For each T1 channel that will answer digital calls, set the Ch n Slot parameters to 9, the default number of the slot that contains the MAX unit's bridge/router module. This tells the MAX to route incoming digital calls to the bridge/router module to be bridged or routed to their destination.
- Press Left-Arrow or Escape to exit the current Line profile.
- In the Confirmation menu, press 2 to save and exit.
EXIT?
>0=ESC (Don't exit)
1=Exit and discard
2=Exit and accept
If you using ISDN signaling, you must perform these additional steps to configure incoming call routing:
- To tell the MAX how to route incoming digital calls, from the main Edit menu select the
slot that contains the digital modem cards. For example, 50-000 V.34 Modem.
50-000 V.34 Modem
50-100 Mod Config
50-200 Modem Diag
- Select Mod Config.
50-000 Mod Config
Module Name=
Ans 1#=
Ans 2#=
Ans 3#=
Ans 4#=
- In the Ans n# parameters enter the rightmost unique digits of the telephone numbers used
by callers using analog devices.
For example, set Ans 1#=1111
This tells the MAX to route all calls coming in from phone number 555-1111 (the hunt group for analog callers) to the digital modems.
- Press Left-Arrow or Escape to exit the current Modem profile.
In the Confirmation menu, press 2 to save and exit.
- Press Left-Arrow or Escape to return to the main Edit menu.
- To tell the MAX how to route incoming digital calls, from the main Edit menu select
Ethernet > Mod Config > WAN Options.
90-C00 Mod Config
WAN options...
Dial Plan=N/A
Ans 1#=
Ans 2#=
Ans 3#=
Ans 4#=
Pool#1 start=0.0.0.0
Pool#1 count=0
Pool#2 start=0.0.0.0
Pool#2 count=0
Pool only=No
Pool Summary=No
- In the Ans n# parameters enter the rightmost unique digits of the telephone numbers used
by callers using analog devices.
For example, set Ans 1#=2222.
This tells the MAX to route all calls coming in from phone number 555-2222 (the hunt group for digital callers) to the MAX Ethernet module.
- If you are going to dynamically assign addresses to incoming callers, set the following
parameters:
- Pool#1 Start. The first IP address in the pool.
- Pool#1 Count. The number of IP addresses in the pool.
- Press Left-Arrow or Escape to exit the Ethernet Mod Config profile.
In the Confirmation menu, press 2 to save and exit.
Those are all the parameters necessary for your T1 line configuration.
After the T1/PRI provider has established service, observe the MAX unit's front panel LEDs (Figure 3-5).
Figure 3-5. Front Panel LEDs
Is the Power LED on and the Fault, Data, and Alarm off?
- If Yes: Continue on to "Configuring the Ethernet profile."
- If No: The connection to the T1/PRI line has failed. If the Alarm LED is on, check your cabling. Also verify with your T1/PRI line provider that you have the correct Framing Mode, Encoding, Length, and Buildout values.
Note: If you must re-enter the parameters for your T1 line, first return all parameter values to
their defaults as listed in the MAX 6000 Series Reference Guide.
Configuring the Ethernet profile
To configure the Ethernet profile:
- From the Main Edit Menu, select Ethernet > Mod Config.
90-B00 Mod Config
Module Name=
Ether options...
WAN options...
SNMP options...
OSPF options...
OSPF global options...
Route Pref...
TServ options...
Bridging=No
Shared Prof=No
Telnet PW=
RIP Policy=Poison Rvrs
RIP Summary=Yes
ICMP Redirects=Accept
BOOTP Relay...
DNS...
- Select Ether options. The following list of parameters appears:
90-C00 Mod Config
>IP Adrs=10.9.8.7
2nd Adrs=0.0.0.0/0
RIP Recv-v1
Ignore Def Rt=Yes
Proxy Mode=Off
Filter=0
IPX Frame=None
IPX Enet#=N/A
IPX Pool#=N/A
IPX SAP Filter=N/A
Handle IPX Type20=N/A
- Enter the IP address /subnet mask of this MAX using the IP Adrs parameter.
- Press Enter to return to the list of parameters.
- Specify how you want the MAX to handle RIP packets on its Ethernet interface using the
RIP parameter:
- Off (the default) specifies that the MAX does not transmit or receive RIP updates.
- Recv-v1: The MAX receives RIP-v1 updates, but does not transmit RIP updates.
- Send-v1: The MAX transmits RIP-v1 updates, but does not receive RIP updates.
- Both-v1: The MAX transmits and receives RIP-v1 updates.
- Send-v2: The MAX transmits RIP-v2 updates, but does not receive RIP updates.
- Recv-v2: The MAX receives RIP-v2 updates, but does not transmit RIP updates.
- Both-v2: The MAX transmits and receives RIP-v2 updates.
- Press Left-Arrow or Escape to exit Ether options submenu.
- At the Confirmation menu, press 2 to save your changes.
EXIT?
>0=ESC (Don't exit)
1=Exit and discard
2=Exit and accept
- Press Escape until you return to the Main Edit Menu.
Configuring the Answer profile
The MAX uses the parameters in the Answer profile to build incoming calls. Note that settings in Connection profiles take precedence over the same settings in the Answer profile.
- From the Main Edit Menu, select Ethernet > Answer.
90-800 Mod Config
>Use Answer as Default=No
Force 56=No
Profile Reqd=Yes
Clid Auth=Ignore
Assign Adrs=No
Encaps...
Ip options...
PPP options...
COMB options...
V.120 options...
Session options...
DHCP options...
- To be able to dynamically assign addresses to incoming callers, make sure Assign
Adrs=Yes.
- Select PPP options.
90-700 Answer
PPP options...
Route IP=Yes
Route IPX=No
Bridge=Yes
Recv Auth=CHAP
MRU=1524
LQM=No
LQM Min=600
LQM Max=600
Link Comp=Stac
VJ Comp=Yes
Dyn Alg=Quadratic
Sec History=15
Add Pers=5
Sub Pers=10
Min Ch Count=1
Max Ch Count=1
- Make sure Route IP=Yes.
- Set the Recv Auth parameter to the authentication you are going to require for incoming
calls:
- None (the default) specifies that the MAX does not use an authentication protocol to validate incoming calls.
- PAP specifies the Password Authentication Protocol, a PPP authentication protocol.
- CHAP specifies the Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol, a more secure PPP authentication protocol.
- MS-CHAP specifies the MAX.
- Either specifies that the MAX can use either CHAP, PAP, or MS-CHAP. The MAX first requests authentication using CHAP. If the dial-in call rejects the request (or does not acknowledge it), the MAX then requests PAP authentication, then MS-CHAP.
- Press Escape or Left-Arrow until the Confirmation menu appears. Press 2 to save your
changes.
- Press Left-Arrow or Escape until you return to the Main Edit Menu.
Creating Connection profiles
Connection profiles define remote users to the MAX.
To create a Connection profile:
- From the Main Edit Menu, select Ethernet > Connections.
90-100 Connections
90-101
90-102
90-103
90-104
90-105
90-106
90-107
90-108
90-109
90-110
90-111
90-111
- Select the first profile. A list of parameters appears:
90-101
Station=
Active=No
Encaps=MPP
PRI # Type=National
Dial #=
Calling #=
Called #=
Route IP=Yes
Route IPX=N/A
Bridge=N/A
Dial brdcast=
Encaps options...
Ip options...
Ipx options...
Session options...
Telco options...
- Select and modify the following parameters:
- Station. Enter a name such as "Remote-Call." This acts as the login name of the remote user.
- Active=Yes.
- Encaps. Set the encapsulation method you want to use for this connection. We recommend you select MPP for this test. If the remote device does not support MPP, the MAX will attempt to negotiate an MP session. If the remote device does not support MP, the MAX will attempt to negotiate a PPP session.
- Route IP=Yes.
- Select Encaps options.
90-101
Encaps options...
Send Auth=None
Send PW=N/A
Aux Send PW=N/A
Recv PW=
DBA Monitor=Transmit
Base Ch Count=1
Min Ch Count=2
Inc Ch Count=1
Dec Ch Count=1
MRU=1524
LQM=No
LQM Min=600
LQM Min=600
Link Comp=Stac
- Select Ip options.
90-101
Ip options...
LAN Adrs=0.0.0.0/0
WAN Alias=0.0.0.0/0
IF Adrs=0.0.0.0/0
Preference=100
Metric=7
Private=No
RIP=Off
Pool=0
Multicast Client=No
Multicast Rate Limit=100
Client Pri DNS-0.0.0.0
Client Sec DNS=0.0.0.0
Client Assign DNS=Yes
- If you are configuring a Connection profile for a device with its own IP address, set the
following parameters:
- LAN Adrs. Enter the IP address / subnet mask of the remote unit, then press Enter to return to the list of parameters.
- WAN Alias. If the far-end device is non-Ascend and requires numbered interfaces with PPP encapsulation, in WAN Alias enter the IP address of the remote unit's WAN interface (not its Ethernet interface), then press Enter to return to the list of parameters.
- IF Adrs. If you are implementing interfaced-based routing on the MAX enter the IP address of the port on the MAX side of the link.
- If you are configuring a Connection profile for dynamic address assignment, set the
following parameter:
- Pool. The IP address pool from which you want to assign this client an address. IP address pools are configured in the Ethernet > Mod Config > WAN options submenu.
- Using the RIP parameter, specify how you want the MAX to handle RIP packets on this
WAN interface:
- Off (the default) specifies that the MAX does not transmit or receive RIP updates.
- Recv-v1: The MAX receives RIP-v1 updates, but does not transmit RIP updates.
- Send-v1: The MAX transmits RIP-v1 updates, but does not receive RIP updates.
- Both-v1: The MAX transmits and receives RIP-v1 updates.
- Send-v2: The MAX transmits RIP-v2 updates, but does not receive RIP updates.
- Recv-v2: The MAX receives RIP-v2 updates, but does not transmit RIP updates.
- Both-v2: The MAX transmits and receives RIP-v2 updates.
- Press Escape or Left-Arrow until the Confirmation menu appears. Press 2 to save your
changes.
- Press Left-Arrow until you return to the Main Edit Menu.
Testing the connections
Testing the connections assumes you have successfully configured the MAX in the previous section. The following tests are involved:
Testing the LAN connection
This test requires that can run Ping or Telnet from a host or workstation on the same subnet as your MAX.
From a host or workstation, open a Telnet session with the MAX or Ping the MAX.
If you open a Telnet session with the MAX, the MAX user interface display should appear. If you have configured a Telnet password in the Ethernet > Mod Config > Telnet PW parameter, the MAX prompts for it before you can access the MAX user interface.
If you are Pinging the MAX, you should get the message that you are immediately receiving a return packet for every packet you are sending to the MAX. If you are not getting the proper response, it might be because of a problem with the LAN, because you entered the wrong IP address, or because of misconfiguration of either the subnet mask or IP Adrs parameter in the Ethernet profile. If the host or workstation is on a different network from the MAX, make sure your IP routing configurations allow the host or workstation to reach the MAX.
Testing the T1/PRI line
To test whether the MAX line is functioning normally, use the Test command from the MAX terminal server. This command causes the MAX to place a call to itself over the WAN, and to send a number of packets over the connection. This tests the MAX unit's ability to initiate and receive calls, and diagnoses whether the connection over the digital access line is functional.
The terminal server Test command uses one channel to dial out and another channel to answer as in the following illustration. This requires that the T1/PRI line is set for bidirectional calling and has two channels available for the test.
Note: The Test command is a basic test of connectivity. It is normal to receive less packets
than the command sends. For example, if the command sends 1000 packets, and receives 994
packets, the test is successful.
To perform a self test:
- From the Main Edit Menu, select System:
00-200 System
00-100 Sys Config
>00-200 Sys Diag
00-300 Security
00-400 Destinations
00-500 Dial Plan
- Select Sys Diag.
00-200 Sys Diag
>00-201 Restore Cfg
00-202 Save Config
00-203 Use MIF
00-204 Sys Reset
00-205 Term Serv
00-206 Upd Rem Cfg
- Select Term Serv.
The Terminal Server screen appears:
** Ascend Pipeline Terminal Server **
ascend%
- Type test phone-number
where phone-number is the phone number of the MAX T1 line.
The most frequent cause for failing to connect is incorrect phone numbers.
Testing the WAN connection
This procedure assumes:
- You can run Telnet or Ping from a host or workstation on the same LAN segment as MAX.
- There is a remote unit (MAX-compatible) to which you can route data packets over a dial-up link.
Note: The remote unit should be configured for the route back to your MAX; otherwise you
might bring up the connection and send packets, but fail to receive anything back.
You test your MAX installation by using Ping or Telnet to and from the remote unit over a dial-up connection as illustrated in Figure 3-6. 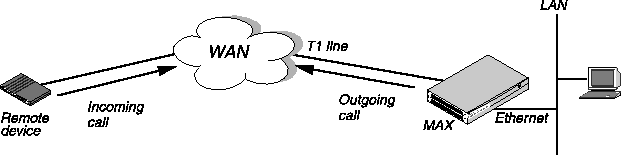
Figure 3-6. Testing the WAN by dialing into and out from the MAX
- Configure the routes of a host on the same LAN as your MAX so that your MAX is the
gateway to the remote unit.
The most common method is to add static routes to the remote unit using your MAX as a gateway. You can also make your MAX the default router.
For example, if the remote unit address is 167.34.9.23, and the your MAX address is 165.3.45.8, the gateway configuration on the remote unit would be:
- Address (remote unit) address 167.34.9.23
- Gateway (your local unit) address 165.3.45.8
- From the local host, enter the Telnet or Ping command for the remote unit.
If you are not getting the proper response, this procedure has failed. It might be because of a problem with the LAN, or because of misconfiguration. Verify the configuration of the Ethernet profile.
- Terminate the Telnet or Ping sessions.
Where to go next
Table 3-10 explains where to find further information about configuring and operating your MAX.
Quickstart for E1 MAX units
With this Quickstart, you will be able to perform a basic configuration of your MAX. It explains how to:
- Configure your MAX for the local Ethernet
- Configure your E1 line for either R2 signaling, DPNSS/DASS-2, or ISDN D-channel signaling.
- Test your E1 line by performing a self test
- Telnet to the MAX from a workstation to verify it is accessible over the Ethernet
- Create a Connection profile on the MAX for a remote device (such as an Ascend Pipeline) dialing in with its own IP address or for a remote device (such as a modem) that accepts a dynamically assigned address
This Quickstart does not cover more detailed configuration such as security, RADIUS, or advanced WAN or LAN protocols. Refer to the MAX 6000 Series ISP & Telecommuting Configuration Guide to perform more advanced configuration of your MAX.
Setting up your hardware
Before beginning, make sure you have:
Figure 3-7 illustrates the hardware set up you must have to use this Quickstart.
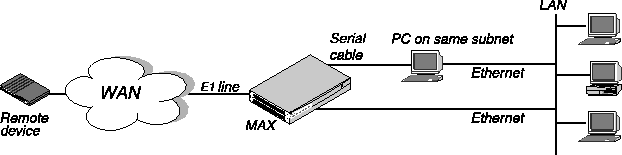
Figure 3-7. Quickstart set up
Overview of E1 line configuration
Figure 3-8 displays two hunt groups-one for digital calls and one for analog calls. If you are using R2 signaling (Figure 3-2), the example hunt group contains 12 channels. Analog callers call in using the phone number 555-1111 and are routed to the digital modems in slot 5. Digital callers call in using the phone number 555-2222 and are routed to the MAX bridge/router module in slot 9. This requires that you configure the Ch n slot parameter in the E1 Line profile.
R2 signaling is less flexible than ISDN D-channel signaling because you must pre-allocate the number of E1channels used for voice and data calls. If 12 analog callers are dialed in, subsequent analog callers are rejected because there are no more channels available for analog calls, even though there are 12 unused channels. 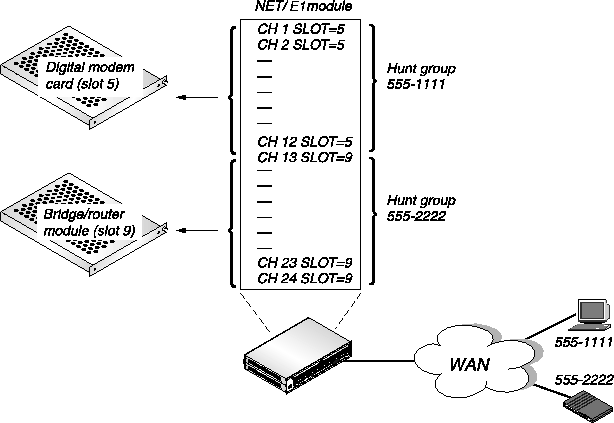
Figure 3-8. Incoming call routing using R2 signaling and hunt groups
If you are using ISDN D-channel signaling (Figure 3-9) the example hunt group contains 24 channels. Analog callers call in using the phone number 555-1111 and are routed to the digital modems in slot 5. Digital callers call in using the phone number 555-2222 and are routed to the MAX bridge/router module in slot 9. This requires that you configure the Ans# parameter in the Modem profile and in the Ethernet Mod Config profile.
Incoming ISDN calls contain information about whether the call is an analog voice call (from a modem) or a digital data call. The MAX can automatically route calls to the digital modem card if the call is a voice call, or to the bridge/router module if the call is a digital call.
With ISDN signaling the hunt groups overlap the E1 channels, allowing each channel to answer either voice calls or data calls.
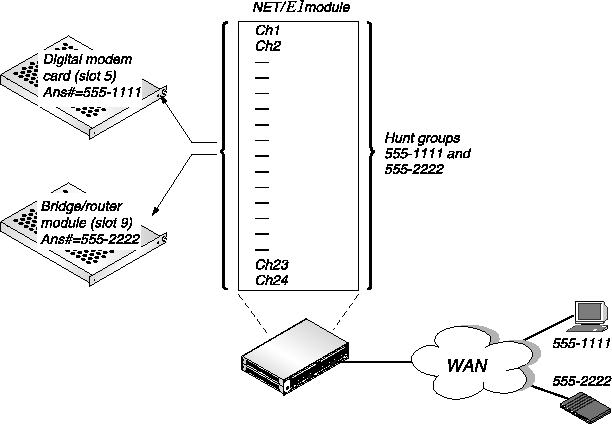
Figure 3-9. Incoming call routing using ISDN signaling and hunt groups
Gathering configuration information
In addition to the hardware set up, you must gather this configuration information about your network set up:
E1 line information
Use information in Table 3-6 to configure the MAX E1 line. You can leave all other parameters in the Line Config profile at their default values for the purposes of this Quickstart Guide.
Refer to the MAX 6000 Series Reference Guide for detailed information on the parameters in the following table.
Table 3-6. E1 line configuration information
NET/E1>Line Config>Line profile parameters
|
Your setting
|
Comments
|
|---|
|
Sig Mode
|
|
Enter the type of signaling your line uses:
- None indicates a leased line.
- ISDN signaling using the D channel. The 32nd channel of the E1 line must be designated as the D channel.
- DPNSS indicates that the interface supports DPNSS or DASS 2 signaling.
- R2 indicates R2 signaling.
- Metered indicates metered R2 signaling protocol, used in Brazil and South Africa.
- Chinese indicates a version of the R2 signaling protocol specified for use in China.
Get this information from your service provider.
|
|
Switch Type
|
|
In a Net/T1 profile, specify one of the following values:
In a Net/E1 profile, specify one of the following values:
- GloBanD (Q.931W GloBanD data service)
- NI-1 (National IDSN-1)
- Net 5 (Euro ISDN services in Belgium, the Netherlands, Switzerland, Sweden, Denmark, and Singapore)
- DASS 2 (U.K. only)
- ISLX (DPNSS switch type)
- ISDX (DPNSS switch type)
- Mercury (DPNSS switch type)
- Australian (Australia only)
- French (VN3 ISDN PRI)
- German (1TR6)
- CAS (New Zealand)
Get this information from your service provider.
|
|
Framing Mode
|
|
For each line, enter G.703 (default) or 2DS. Get this information from your service provider.
|
|
Length ?
|
|
If your MAX does not have an internal CSU, enter the cable length from the CSU or other network interface to the MAX.
|
Connection profile information
The MAX uses Connection profiles to allow access to remote devices. For this test you can set up two kinds of connections:
- A Connection profile for a remote device (such as an Ascend Pipeline) dialing in with its own IP address
- A Connection profile for a remote device (such as a modem) that accepts a dynamically assigned address
Use information in Table 3-7 to create a connection to a remote device. You can leave all other parameters in the Connection profile at their default values for the purposes of this Quickstart Guide. Refer to the MAX 6000 Series Reference Guide for detailed information on the parameters in the following table.
Ethernet profile information
Use information in Table 3-8 to configure the MAX for your Ethernet LAN. You can leave all other parameters in the Ethernet > Mod Config profile at their default values for the purposes of this Quickstart Guide. Refer to the MAX 6000 Series Reference Guide for detailed information on the parameters in the following table.
Using the MAX VT-100 interface
This section briefly introduces the MAX configuration interface. Refer to the Chapter 4, "Navigating the User Interface," for complete information on using this interface.
To perform the initial configuration of the MAX, connect a serial cable to the MAX control port and set your terminal emulation package in your communications software as follows:
- 9600 bps
- 8 data bits
- No parity
- 1 stop bit
- No flow control
- Direct connect
After communication has been established, the Control Monitor screen appears (see Figure 3-10). This interface consists of an Edit menu and eight status displays. The Edit menu allows you to configure the MAX; the status windows allow you to monitor the MAX status.
Note that the items listed in the Main Edit menu differ depending on the system configuration.
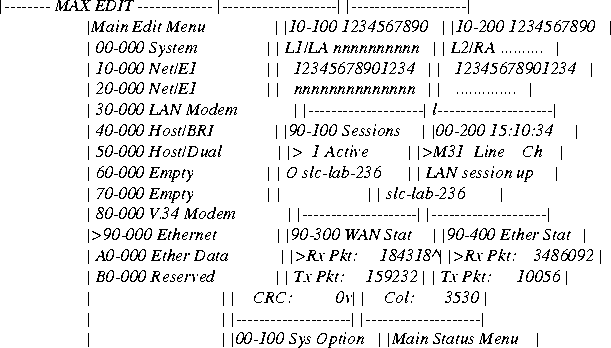
Figure 3-10. MAX configuration interface
The table below provides a quick reference for navigating the MAX user interface.
Configuring the MAX
The following configuration establishes enough functionality to verify that the MAX is up and running, connected, and can perform basic functions. You must perform the tasks in the order they are presented in this section.
The Quickstart configuration involves modifying the following profiles:
This procedure assumes you have not yet configured the MAX; therefore, all parameters initially are at their factory default settings. Do not turn the MAX off during this procedure.
Note: The question marks (??) that may appear in the upper right-hand corner of the Edit
screens and status windows indicate that there is no link to the E1/PRI line. Once you have
configured the E1/PRI line these question marks will disappear.
Configuring the E1/PRI lines
To configure a E1 line with the information you gathered in Table 3-6:
- From the Main Edit Menu, select the slot that contains your Net/E1 card, for example, 10-
000.
10-000 Net/E1
>10-100 Line Config
10-200 Line Diag
- Select Line Config.
10-100 Line Config
>10-1** Factory
10-102
10-103
10-104
- Select the currently active Line profile, 10-1** Factory.
10-1** Factory
>Name=
1st Line=Trunk
2nd Line=Disabled
Line 1...
Line 2...
- Select Line 1.
10-1** Factory
Line 1...
>Sig Mode=Inband ^
NFAS ID num=N/A
Rob Ctl=Wink-Start
Switch Type=N/A
Framing Mode=D4
Encoding=AMI
FDL=N/A
Length=N/A
Buildout=0 dB
Clock Source=Yes
Pbx Type=N/A
Delete Digits=N/A
Add Number=N/A
Call-by-Call=N/A
Ans #=N/A
- Set the appropriate signaling mode for Sig Mode parameter:
- None indicates a leased line.
- ISDN signaling using the D channel. The 32nd channel of the E1 line must be designated as the D channel.
- DPNSS indicates that the interface supports DPNSS or DASS 2 signaling.
- R2 indicates R2 signaling.
- Metered indicates metered R2 signaling protocol, used in Brazil and South Africa.
- Chinese indicates a version of the R2 signaling protocol specified for use in China.
- If you selected ISDN above, select the WAN switch type at the lines' point-of-presence.
- N/A: This parameter is not applicable whenever Sig Mode=Inband.
- AT&T
- NTI
- NI-2
- GloBanD
- Japan
- Select the type of framing this line uses:
- Select the encoding used on this line:
- None: This is identical to AMI, but without density enforcement.
- AMI
- B8ZS
- Select the FDL (Facility Data Link) used on this line:
- N/A: This parameter is not applicable whenever Framing Mode=D4.
- None
- AT&T
- ANSI
- Sprint
- Select the cable distance between MAX and the WAN interface equipment.
- N/A: This parameter is N/A if the MAX has an internal CSU.
- Otherwise: Select the correct cable distance in feet between MAX and the CSU or other network (WAN) interface unit to which it is connected. The default is 1-133.
- Select the amount of attenuation to add to the line's network interface:
- N/A: This parameter is N/A if the MAX does not have an internal CSU.
- Otherwise: Select the Buildout value to provide the proper line attenuation. The default is 0db.
- If your channels are not switched (the default), specify how the MAX uses the E1
channels using the Ch n parameter:
- Switched (the default)
- Nailed (dedicated)
- Unused (not in service)
Note: To test the line later, you must have at least two switched channels. If you plan to
use a channel for drop-and-insert (D&I), you can enter it as Switched for the Quickstart
and then change it to D&I for the final installation.
- If you using R2 signaling, configure incoming call routing for the E1 line by setting the
following parameters:
- For each Ch n # parameter, enter the rightmost unique digits of the phone number used to reach this channel.
- For example, if your line is set up as illustrated in Figure 3-8 on page 3-23, enter 1111 for the first 12 channels (the analog call hunt group), and 2222 for the last 12 channels (the digital call hunt group).
- For each E1 channel that will answer analog calls, set the Ch n Slot parameters to the number of the slot that contains the modem card.
- For example, if the modem card is in slot 5, set Ch 1 Slot=5, Ch 2 Slot=5, and so on, up to the total number of analog calls you want the MAX to accept on this E1 line. This tells the MAX to route incoming analog calls to the digital modem card.
- For each E1 channel that will answer digital calls, set the Ch n Slot parameters to 9, the default number of the slot that contains the MAX unit's bridge/router module. This tells the MAX to route incoming digital calls to the bridge/router module to be bridged or routed to their destination.
- Press Left-Arrow or Escape to exit the current Line profile.
- In the Confirmation menu, press 2 to save and exit.
EXIT?
>0=ESC (Don't exit)
1=Exit and discard
2=Exit and accept
If you are using ISDN signaling, you must perform these additional steps to configure incoming call routing:
- To tell the MAX how to route incoming digital calls, from the main Edit menu select the
slot that contains the digital modem cards. For example, 50-000 V.34 Modem.
50-000 V.34 Modem
50-100 Mod Config
50-200 Modem Diag
- Select Mod Config.
50-000 Mod Config
Module Name=
Ans 1#=
Ans 2#=
Ans 3#=
Ans 4#=
- In the Ans n# parameters enter the rightmost unique digits of the telephone numbers used
by callers using analog devices.
For example, set Ans 1#=1111
This tells the MAX to route all calls coming in from phone number 555-1111 (the hunt group for analog callers) to the digital modems.
- Press Left-Arrow or Escape to exit the current Modem profile.
In the Confirmation menu, press 2 to save and exit.
- Press Left-Arrow or Escape to return to the main Edit menu.
- To tell the MAX how to route incoming digital calls, from the main Edit menu select
Ethernet > Mod Config > WAN Options.
90-C00 Mod Config
WAN options...
Dial Plan=N/A
Ans 1#=
Ans 2#=
Ans 3#=
Ans 4#=
Pool#1 start=0.0.0.0
Pool#1 count=0
Pool#2 start=0.0.0.0
Pool#2 count=0
Pool only=No
Pool Summary=No
- In the Ans n# parameters enter the rightmost unique digits of the telephone numbers used
by callers using analog devices.
For example, set Ans 1#=2222.
This tells the MAX to route all calls coming in from phone number 555-2222 (the hunt group for digital callers) to the MAX Ethernet module.
- If you are going to dynamically assign addresses to incoming callers, set the following
parameters:
- Pool#1 Start. The first IP address in the pool.
- Pool#1 Count. The number of IP addresses in the pool.
- Press Left-Arrow or Escape to exit the Ethernet Mod Config profile.
In the Confirmation menu, press 2 to save and exit.
Those are all the parameters necessary for your E1 line configuration.
After the E1/PRI provider has established service, observe the MAX unit's front panel LEDs (Figure 3-11).
Figure 3-11. Front Panel LEDs
Is the Power LED on and the Fault, Data, and Alarm off?
- If Yes: Continue on to "Configuring the Ethernet profile."
- If No: The connection to the E1/PRI line has failed. If the Alarm LED is on, check your cabling. Also verify with your E1/PRI line provider that you have the correct Framing Mode, Encoding, Length, and Buildout values.
Note: If you must re-enter the parameters for your E1 line, first return all parameter values to
their defaults as listed in the MAX 6000 Series Reference Guide.
Configuring the Ethernet profile
To configure the Ethernet profile:
- From the Main Edit Menu, select Ethernet > Mod Config.
90-B00 Mod Config
Module Name=
Ether options...
WAN options...
SNMP options...
OSPF options...
OSPF global options...
Route Pref...
TServ options...
Bridging=No
Shared Prof=No
Telnet PW=
RIP Policy=Poison Rvrs
RIP Summary=Yes
ICMP Redirects=Accept
BOOTP Relay...
DNS...
- Select Ether options. The following list of parameters appears:
90-C00 Mod Config
>IP Adrs=10.9.8.7
2nd Adrs=0.0.0.0/0
RIP Recv-v1
Ignore Def Rt=Yes
Proxy Mode=Off
Filter=0
IPX Frame=None
IPX Enet#=N/A
IPX Pool#=N/A
IPX SAP Filter=N/A
Handle IPX Type20=N/A
- Enter the IP address /subnet mask of this MAX using the IP Adrs parameter.
- Press Enter to return to the list of parameters.
- Specify how you want the MAX to handle RIP packets on its Ethernet interface using the
RIP parameter:
- Off (the default) specifies that the MAX does not transmit or receive RIP updates.
- Recv-v1: The MAX receives RIP-v1 updates, but does not transmit RIP updates.
- Send-v1: The MAX transmits RIP-v1 updates, but does not receive RIP updates.
- Both-v1: The MAX transmits and receives RIP-v1 updates.
- Send-v2: The MAX transmits RIP-v2 updates, but does not receive RIP updates.
- Recv-v2: The MAX receives RIP-v2 updates, but does not transmit RIP updates.
- Both-v2: The MAX transmits and receives RIP-v2 updates.
- Press Left-Arrow or Escape to exit Ether options submenu.
- At the Confirmation menu, press 2 to save your changes.
EXIT?
>0=ESC (Don't exit)
1=Exit and discard
2=Exit and accept
- Press Escape until you return to the Main Edit Menu.
Configuring the Answer profile
The MAX uses the parameters in the Answer profile to build incoming calls. Note that settings in Connection profiles take precedence over the same settings in the Answer profile.
- From the Main Edit Menu, select Ethernet > Answer.
90-800 Mod Config
>Use Answer as Default=No
Force 56=No
Profile Reqd=Yes
Clid Auth=Ignore
Assign Adrs=No
Encaps...
Ip options...
PPP options...
COMB options...
V.120 options...
Session options...
DHCP options...
- To be able to dynamically assign addresses to incoming callers, make sure Assign
Adrs=Yes.
- Select PPP options.
90-700 Answer
PPP options...
Route IP=Yes
Route IPX=No
Bridge=Yes
Recv Auth=CHAP
MRU=1524
LQM=No
LQM Min=600
LQM Max=600
Link Comp=Stac
VJ Comp=Yes
Dyn Alg=Quadratic
Sec History=15
Add Pers=5
Sub Pers=10
Min Ch Count=1
Max Ch Count=1
- Make sure Route IP=Yes.
- Set the Recv Auth parameter to the authentication you are going to require for incoming
calls:
- None (the default) specifies that the MAX does not use an authentication protocol to validate incoming calls.
- PAP specifies the Password Authentication Protocol, a PPP authentication protocol.
- CHAP specifies the Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol, a more secure PPP authentication protocol.
- MS-CHAP specifies the MAX.
- Either specifies that the MAX can use either CHAP, PAP, or MS-CHAP. The MAX first requests authentication using CHAP. If the dial-in call rejects the request (or does not acknowledge it), the MAX then requests PAP authentication, then MS-CHAP.
- Press Escape or Left-Arrow until the Confirmation menu appears. Press 2 to save your
changes.
- Press Left-Arrow or Escape until you return to the Main Edit Menu.
Creating Connection profiles
Connection profiles define remote users to the MAX.
To create a Connection profile:
- From the Main Edit Menu, select Ethernet > Connections.
90-100 Connections
90-101
90-102
90-103
90-104
90-105
90-106
90-107
90-108
90-109
90-110
90-111
90-111
- Select the first profile. A list of parameters appears:
90-101
Station=
Active=No
Encaps=MPP
PRI # Type=National
Dial #=
Calling #=
Called #=
Route IP=Yes
Route IPX=N/A
Bridge=N/A
Dial brdcast=
Encaps options...
Ip options...
Ipx options...
Session options...
Telco options...
- Select and modify the following parameters:
- Station. Enter a name such as "Remote-Call." This acts as the login name of the remote user.
- Active=Yes.
- Encaps. Set the encapsulation method you want to use for this connection. We recommend you select MPP for this test. If the remote device does not support MPP, the MAX will attempt to negotiate an MP session. If the remote device does not support MP, the MAX will attempt to negotiate a PPP session.
- Route IP=Yes.
- Select Encaps options.
90-101
Encaps options...
Send Auth=None
Send PW=N/A
Aux Send PW=N/A
Recv PW=
DBA Monitor=Transmit
Base Ch Count=1
Min Ch Count=2
Inc Ch Count=1
Dec Ch Count=1
MRU=1524
LQM=No
LQM Min=600
LQM Min=600
Link Comp=Stac
- Select Ip options.
90-101
Ip options...
LAN Adrs=0.0.0.0/0
WAN Alias=0.0.0.0/0
IF Adrs=0.0.0.0/0
Preference=100
Metric=7
Private=No
RIP=Off
Pool=0
Multicast Client=No
Multicast Rate Limit=100
Client Pri DNS-0.0.0.0
Client Sec DNS=0.0.0.0
Client Assign DNS=Yes
- If you are configuring a Connection profile for a device with its own IP address, set the
following parameters:
- LAN Adrs. Enter the IP address / subnet mask of the remote unit, then press Enter to return to the list of parameters.
- WAN Alias. If the far-end device is non-Ascend and requires numbered interfaces with PPP encapsulation, in WAN Alias enter the IP address of the remote unit's WAN interface (not its Ethernet interface), then press Enter to return to the list of parameters.
- IF Adrs. If you are implementing interfaced-based routing on the MAX enter the IP address of the port on the MAX side of the link.
- If you are configuring a Connection profile for dynamic address assignment, set the
following parameter:
- Pool. The IP address pool from which you want to assign this client an address. IP address pools are configured in the Ethernet > Mod Config > WAN options submenu.
- Using the RIP parameter, specify how you want the MAX to handle RIP packets on this
WAN interface:
- Off (the default) specifies that the MAX does not transmit or receive RIP updates.
- Recv-v1: The MAX receives RIP-v1 updates, but does not transmit RIP updates.
- Send-v1: The MAX transmits RIP-v1 updates, but does not receive RIP updates.
- Both-v1: The MAX transmits and receives RIP-v1 updates.
- Send-v2: The MAX transmits RIP-v2 updates, but does not receive RIP updates.
- Recv-v2: The MAX receives RIP-v2 updates, but does not transmit RIP updates.
- Both-v2: The MAX transmits and receives RIP-v2 updates.
- Press Escape or Left-Arrow until the Confirmation menu appears. Press 2 to save your
changes.
- Press Left-Arrow until you return to the Main Edit Menu.
Testing the connections
Testing the connections assumes you have successfully configured the MAX in the previous section. The following tests are involved:
Testing the LAN connection
This test requires that can run Ping or Telnet from a host or workstation on the same subnet as your MAX.
The following illustration shows how to test the Ethernet interface of your MAX by Pinging or Telneting to it from a station on the same LAN. 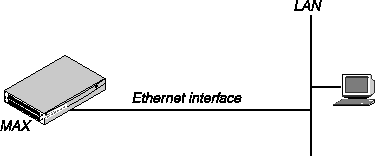
Figure 3-12. Testing the LAN Interface with Telnet or Ping
- From a host or workstation, on the same subnet as MAX, Telnet to or Ping the MAX.
- If you are running Telnet, the MAX user interface display should appear. The default Telnet password for an unconfigured MAX is null (a carriage return).
- If you are running Ping, you should get the message that you are immediately receiving a return packet for every packet you are sending to the MAX. If you are not getting the proper response, this procedure has failed. It might be because of a problem with the LAN, because you entered the wrong IP address, or because of misconfiguration of either the subnet mask or IP Adrs parameter in the Ethernet profile.
- Terminate the Telnet or Ping sessions.
Testing the E1/PRI line
To test whether the MAX line is functioning normally, use the Test command from the MAX terminal server. This command causes the MAX to place a call to itself over the WAN, and to send a number of packets over the connection. This tests the MAX unit's ability to initiate and receive calls, and diagnoses whether the connection over the digital access line is functional.
Note: The terminal server Test command uses one channel to dial out and another channel to
answer as in the following illustration. This requires that the E1/PRI line is set for bidirectional
calling.
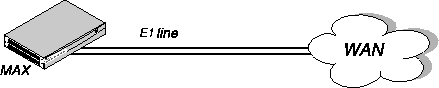
Figure 3-13. Testing the WAN interface by placing a call to yourself
To perform a self test:
- From the Main Edit Menu, select System:
00-200 System
00-100 Sys Config
>00-200 Sys Diag
00-300 Security
00-400 Destinations
00-500 Dial Plan
- Select Sys Diag.
00-200 Sys Diag
>00-201 Restore Cfg
00-202 Save Config
00-203 Use MIF
00-204 Sys Reset
00-205 Term Serv
00-206 Upd Rem Cfg
- Select Term Serv.
The Terminal Server screen appears:
** Ascend Pipeline Terminal Server **
ascend%
- Type test phone-number
where phone-number is the phone number of the MAX E1 line.
The most frequent cause for failing to connect is incorrect phone numbers.
Testing the WAN connection
This procedure assumes:
- You can run Telnet or Ping from a host or workstation on the same LAN segment as MAX.
- There is a remote unit (MAX-compatible) to which you can route data packets over a dial-up link.
Note: The remote unit should be configured for the route back to your MAX; otherwise you
might bring up the connection and send packets, but fail to receive anything back.
You test your MAX installation by using Ping or Telnet to and from the remote unit over a dial-up connection as illustrated in Figure 3-14. 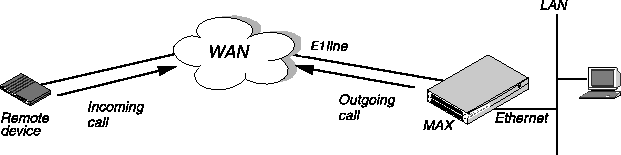
Figure 3-14. Testing the WAN by dialing into and out from the MAX
- Configure the routes of a host on the same LAN as your MAX so that your MAX is the
gateway to the remote unit.
The most common method is to add static routes to the remote unit using your MAX as a gateway. You can also make your MAX the default router.
For example, if the remote unit address is 167.34.9.23, and the your MAX address is 165.3.45.8, the gateway configuration on the remote unit would be:
- Address (remote unit) address 167.34.9.23
- Gateway (your local unit) address 165.3.45.8
- From the local host, enter the Telnet or Ping command for the remote unit.
If you are not getting the proper response, this procedure has failed. It might be because of a problem with the LAN, or because of misconfiguration. Verify the configuration of the Ethernet profile.
- Terminate the Telnet or Ping sessions.
Where to go next
Table 3-10 explains where to find further information about configuring and operating your MAX.
![[Top]](../../images/home.jpg)
![[Contents]](../../images/contents.jpg)
![[Prev]](../../images/previous.jpg)
![[Next]](../../images/next.jpg)
![[Last]](../../images/index.jpg)


techpubs@eng.ascend.com
Copyright © 1998, Ascend Communications, Inc. All rights
reserved.











